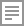
Planetary Boundaries
In 2009 scientists identified nine ‘Planetary Boundaries’ in which humanity can safely live on the planet. This methodology was later updated in 2015. It aims to define the environmental limits in which humanity can safely operate and thrive. The scientifically based framework identifies the safe operating space of humanity on Earth. The nine Planetary Boundaries are: Stratospheric ozone depletion; Loss of biosphere integrity (biodiversity loss and extinctions); Chemical pollution and the release of novel entities; Climate Change; Ocean acidification; Freshwater consumption and the global hydrological cycle; Land system change; Nitrogen and phosphorus flows to the biosphere and oceans; and Atmospheric aerosol loading. Unfortunately, mankind is currently exceeding several of those boundaries.
ICL, as an international chemical company with a range of activities that cover all stages of the product life cycle, from the production of raw materials through their final use in end markets, considers, develops and maintains within its project plans and designs the requirement for environmental protection at all stages of activity, i.e. “Product Stewardship”. ICL’s activities relate to some of the planetary boundaries. With respect to climate change, ICL has set a goal to decrease our GHG emissions and increase renewable energy usage. ICL’s main products are fertilizers, especially phosphate and potash-based fertilizers. Correct use of ICL’s products can prevent leaching of excess nitrogen and enable the continued use of farmland, which, in turn, decreases land-system change. ICL is training farmers as to the balanced use of fertilizers. Regarding stratospheric ozone depletion, as producers of methyl bromide (a substance that is listed in international agreements as a contributor to ozone depletion), ICL is carefully tracking this product and has decreased its production.